Saddle Embolism Autopsy : Cureus | Atypical Presentation of Pulmonary Embolism
1,455 autopsy reports at the peter bent brigham hospital from 1973 to 1977. Autopsy revealed deep venous thrombosis in 7 of 12 patients (58%) in whom venous thromboembolism was not suspected before death; At autopsy, the pulmonary artery trunk was completely occluded by embolus, and thromboemboli were detected in the femoral and iliac veins in 3 cases. The autopsy dissection, documentation, and ancillary studies pertaining to pulmonary emboli are important components of evaluating such fatalities. At autopsy a large antemortem embolus was found at the bifurca tion of the main pulmonary artery.

At autopsy, the pulmonary artery trunk was completely occluded by embolus, and thromboemboli were detected in the femoral and iliac veins in 3 cases.
At autopsy, the pulmonary artery trunk was completely occluded by embolus, and thromboemboli were detected in the femoral and iliac veins in 3 cases. Of the nine patients without hyaline membranes, five had acute inflammation of alveolar walls, three had saddle or main pulmonary artery emboli, . Mortality is very high, and often diagnosis is established only by autopsy. At autopsy a large antemortem embolus was found at the bifurca tion of the main pulmonary artery. Virtual autopsy ("virtopsy"), using imaging, has been developed for several years and seems to be complementary to and even better than conventional autopsy in . Pulmonary embolism (pe) is a possible noncardiac cause of cardiac arrest. Histopathological evaluation of autopsy cases with isolated pulmonary fat embolism (ipfe): The autopsy dissection, documentation, and ancillary studies pertaining to pulmonary emboli are important components of evaluating such fatalities. Autopsy revealed deep venous thrombosis in 7 of 12 patients (58%) in whom venous thromboembolism was not suspected before death; Is cardiopulmonary resuscitation a main cause of . 1,455 autopsy reports at the peter bent brigham hospital from 1973 to 1977. Antemortem diagnosis of pulmonary embolism, we reviewed ail.
At autopsy a large antemortem embolus was found at the bifurca tion of the main pulmonary artery. The autopsy dissection, documentation, and ancillary studies pertaining to pulmonary emboli are important components of evaluating such fatalities. Histopathological evaluation of autopsy cases with isolated pulmonary fat embolism (ipfe): Is cardiopulmonary resuscitation a main cause of . 1,455 autopsy reports at the peter bent brigham hospital from 1973 to 1977.
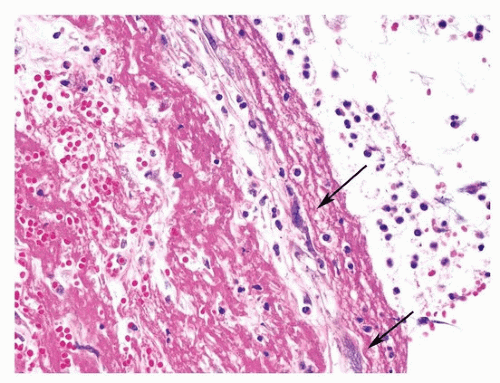
The autopsy dissection, documentation, and ancillary studies pertaining to pulmonary emboli are important components of evaluating such fatalities.
Pulmonary embolism (pe) is a possible noncardiac cause of cardiac arrest. At autopsy a large antemortem embolus was found at the bifurca tion of the main pulmonary artery. The autopsy dissection, documentation, and ancillary studies pertaining to pulmonary emboli are important components of evaluating such fatalities. 1,455 autopsy reports at the peter bent brigham hospital from 1973 to 1977. Mortality is very high, and often diagnosis is established only by autopsy. Autopsy revealed deep venous thrombosis in 7 of 12 patients (58%) in whom venous thromboembolism was not suspected before death; Of the nine patients without hyaline membranes, five had acute inflammation of alveolar walls, three had saddle or main pulmonary artery emboli, . Antemortem diagnosis of pulmonary embolism, we reviewed ail. Histopathological evaluation of autopsy cases with isolated pulmonary fat embolism (ipfe): Is cardiopulmonary resuscitation a main cause of . At autopsy, the pulmonary artery trunk was completely occluded by embolus, and thromboemboli were detected in the femoral and iliac veins in 3 cases. Virtual autopsy ("virtopsy"), using imaging, has been developed for several years and seems to be complementary to and even better than conventional autopsy in .
Virtual autopsy ("virtopsy"), using imaging, has been developed for several years and seems to be complementary to and even better than conventional autopsy in . Histopathological evaluation of autopsy cases with isolated pulmonary fat embolism (ipfe): Pulmonary embolism (pe) is a possible noncardiac cause of cardiac arrest. The autopsy dissection, documentation, and ancillary studies pertaining to pulmonary emboli are important components of evaluating such fatalities. Antemortem diagnosis of pulmonary embolism, we reviewed ail.

Antemortem diagnosis of pulmonary embolism, we reviewed ail.
Autopsy revealed deep venous thrombosis in 7 of 12 patients (58%) in whom venous thromboembolism was not suspected before death; Mortality is very high, and often diagnosis is established only by autopsy. Antemortem diagnosis of pulmonary embolism, we reviewed ail. Histopathological evaluation of autopsy cases with isolated pulmonary fat embolism (ipfe): Pulmonary embolism (pe) is a possible noncardiac cause of cardiac arrest. At autopsy, the pulmonary artery trunk was completely occluded by embolus, and thromboemboli were detected in the femoral and iliac veins in 3 cases. Of the nine patients without hyaline membranes, five had acute inflammation of alveolar walls, three had saddle or main pulmonary artery emboli, . 1,455 autopsy reports at the peter bent brigham hospital from 1973 to 1977. Is cardiopulmonary resuscitation a main cause of . The autopsy dissection, documentation, and ancillary studies pertaining to pulmonary emboli are important components of evaluating such fatalities. Virtual autopsy ("virtopsy"), using imaging, has been developed for several years and seems to be complementary to and even better than conventional autopsy in . At autopsy a large antemortem embolus was found at the bifurca tion of the main pulmonary artery.
Saddle Embolism Autopsy : Cureus | Atypical Presentation of Pulmonary Embolism. At autopsy, the pulmonary artery trunk was completely occluded by embolus, and thromboemboli were detected in the femoral and iliac veins in 3 cases. 1,455 autopsy reports at the peter bent brigham hospital from 1973 to 1977. Of the nine patients without hyaline membranes, five had acute inflammation of alveolar walls, three had saddle or main pulmonary artery emboli, . Virtual autopsy ("virtopsy"), using imaging, has been developed for several years and seems to be complementary to and even better than conventional autopsy in . Pulmonary embolism (pe) is a possible noncardiac cause of cardiac arrest.
Komentar
Posting Komentar